Expo
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AICritical CareSurgical TechniquesPatient Care
Point of CareBusiness
Events

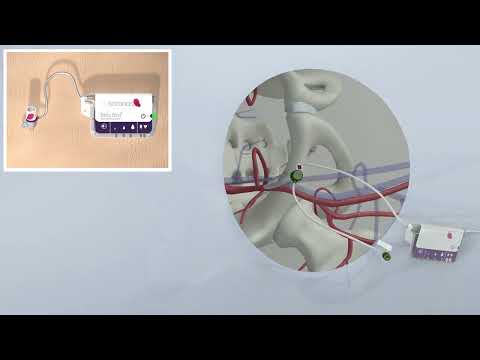
- Breakthrough Technology Combines Detection and Treatment of Nerve-Related Disorders in Single Procedure
- Plasma Irradiation Promotes Faster Bone Healing
- New Device Treats Acute Kidney Injury from Sepsis
- Study Confirms Safety of DCB-Only Strategy for Treating De Novo Left Main Coronary Artery Disease
- Revascularization Improves Quality of Life for Patients with Chronic Limb Threatening Ischemia
- Wearable Technology Monitors and Analyzes Surgeons' Posture during Long Surgical Procedures
- Custom 3D-Printed Orthopedic Implants Transform Joint Replacement Surgery
- Cutting-Edge Imaging Platform Detects Residual Breast Cancer Missed During Lumpectomy Surgery
- Computational Models Predict Heart Valve Leakage in Children
- World’s First Microscopic Probe to Revolutionize Early Cancer Diagnosis
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- Next Gen ICU Bed to Help Address Complex Critical Care Needs
- Groundbreaking AI-Powered UV-C Disinfection Technology Redefines Infection Control Landscape
- Clean Hospitals Can Reduce Antibiotic Resistance, Save Lives
- Smart Hospital Beds Improve Accuracy of Medical Diagnosis
- Mindray to Acquire Chinese Medical Device Company APT Medical
- Olympus Acquires Korean GI Stent Maker Taewoong Medical
- Karl Storz Acquires British AI Specialist Innersight Labs
- Stryker to Acquire French Joint Replacement Company SERF SAS
- Medical Illumination Acquires Surgical Lighting Specialist Isolux
- Strategic Collaboration to Develop and Integrate Generative AI into Healthcare
- AI-Enabled Operating Rooms Solution Helps Hospitals Maximize Utilization and Unlock Capacity
- AI Predicts Pancreatic Cancer Three Years before Diagnosis from Patients’ Medical Records
- First Fully Autonomous Generative AI Personalized Medical Authorizations System Reduces Care Delay
- Electronic Health Records May Be Key to Improving Patient Care, Study Finds
- AI Diagnostic Tool Accurately Detects Valvular Disorders Often Missed by Doctors
- New Model Predicts 10 Year Breast Cancer Risk
- AI Tool Accurately Predicts Cancer Three Years Prior to Diagnosis
- Ground-Breaking Tool Predicts 10-Year Risk of Esophageal Cancer
- AI Tool Analyzes Capsule Endoscopy Videos for Accurately Predicting Patient Outcomes for Crohn’s Disease
- Point of Care HIV Test Enables Early Infection Diagnosis for Infants
- Whole Blood Rapid Test Aids Assessment of Concussion at Patient's Bedside
- New Generation Glucose Hospital Meter System Ensures Accurate, Interference-Free and Safe Use
- Unique Quantitative Diagnostic System Enables Immediate Diagnosis and Treatment at POC
- POC Myocardial Infarction Test Delivers Results in 17 Minutes

 Expo
Expo
- Breakthrough Technology Combines Detection and Treatment of Nerve-Related Disorders in Single Procedure
- Plasma Irradiation Promotes Faster Bone Healing
- New Device Treats Acute Kidney Injury from Sepsis
- Study Confirms Safety of DCB-Only Strategy for Treating De Novo Left Main Coronary Artery Disease
- Revascularization Improves Quality of Life for Patients with Chronic Limb Threatening Ischemia
- Wearable Technology Monitors and Analyzes Surgeons' Posture during Long Surgical Procedures
- Custom 3D-Printed Orthopedic Implants Transform Joint Replacement Surgery
- Cutting-Edge Imaging Platform Detects Residual Breast Cancer Missed During Lumpectomy Surgery
- Computational Models Predict Heart Valve Leakage in Children
- World’s First Microscopic Probe to Revolutionize Early Cancer Diagnosis
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- Next Gen ICU Bed to Help Address Complex Critical Care Needs
- Groundbreaking AI-Powered UV-C Disinfection Technology Redefines Infection Control Landscape
- Clean Hospitals Can Reduce Antibiotic Resistance, Save Lives
- Smart Hospital Beds Improve Accuracy of Medical Diagnosis
- Mindray to Acquire Chinese Medical Device Company APT Medical
- Olympus Acquires Korean GI Stent Maker Taewoong Medical
- Karl Storz Acquires British AI Specialist Innersight Labs
- Stryker to Acquire French Joint Replacement Company SERF SAS
- Medical Illumination Acquires Surgical Lighting Specialist Isolux
- Strategic Collaboration to Develop and Integrate Generative AI into Healthcare
- AI-Enabled Operating Rooms Solution Helps Hospitals Maximize Utilization and Unlock Capacity
- AI Predicts Pancreatic Cancer Three Years before Diagnosis from Patients’ Medical Records
- First Fully Autonomous Generative AI Personalized Medical Authorizations System Reduces Care Delay
- Electronic Health Records May Be Key to Improving Patient Care, Study Finds
- AI Diagnostic Tool Accurately Detects Valvular Disorders Often Missed by Doctors
- New Model Predicts 10 Year Breast Cancer Risk
- AI Tool Accurately Predicts Cancer Three Years Prior to Diagnosis
- Ground-Breaking Tool Predicts 10-Year Risk of Esophageal Cancer
- AI Tool Analyzes Capsule Endoscopy Videos for Accurately Predicting Patient Outcomes for Crohn’s Disease
- Point of Care HIV Test Enables Early Infection Diagnosis for Infants
- Whole Blood Rapid Test Aids Assessment of Concussion at Patient's Bedside
- New Generation Glucose Hospital Meter System Ensures Accurate, Interference-Free and Safe Use
- Unique Quantitative Diagnostic System Enables Immediate Diagnosis and Treatment at POC
- POC Myocardial Infarction Test Delivers Results in 17 Minutes























.jpg)













